Image Classification in ML
Prerequisites: Machine Learning Terminology
Semantic Gap#
In order to train a Machine Learning Model that can classify images, we need to first overcome a few challenges, commonly known as the Semantic Gap
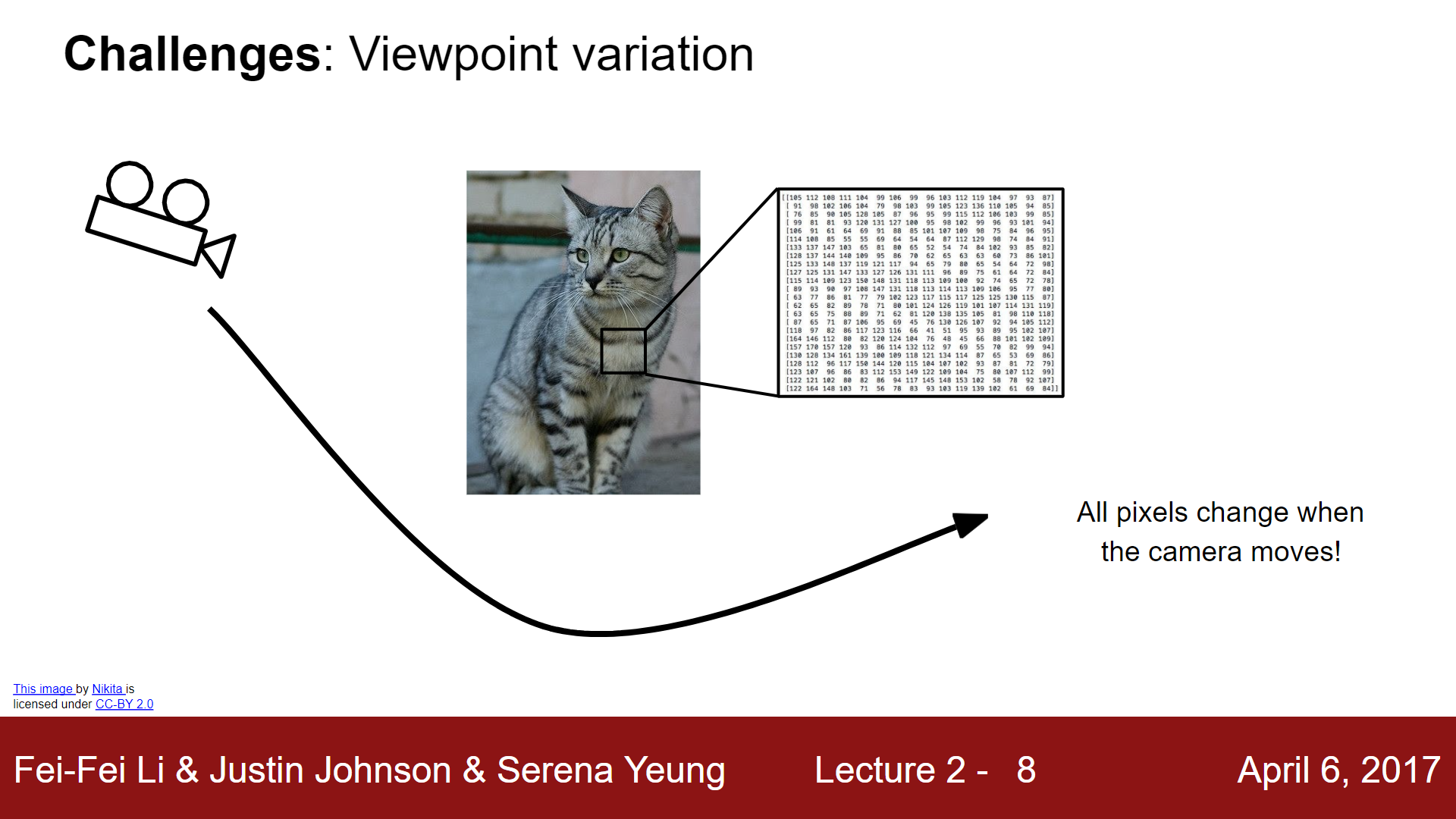
When the computer is given an image, it reads the data as a 3d-matrix/array defined by its dimensions and RGB pixels. A typical matrix size would be [800, 600, 3], with the 800 and 600 being dimensions and the 3 representing the 3 RGB (red, green blue) channels.
Viewpoint Variation#
If the “camera” is rotated or moved when taking a picture, all pixels will change.
Illumination#
Similarly, the lighting of the photo can also affect the picture.

Deformation#
Objects can also be “deformed”, and photos can contain objects with an unusual appearance.

Occlusion#
Objects can also be occluded or blocked by other objects. For example, a cat under a couch cushion would be hard for a computer distinguish, although humans can instantly recognize that there is a cat.

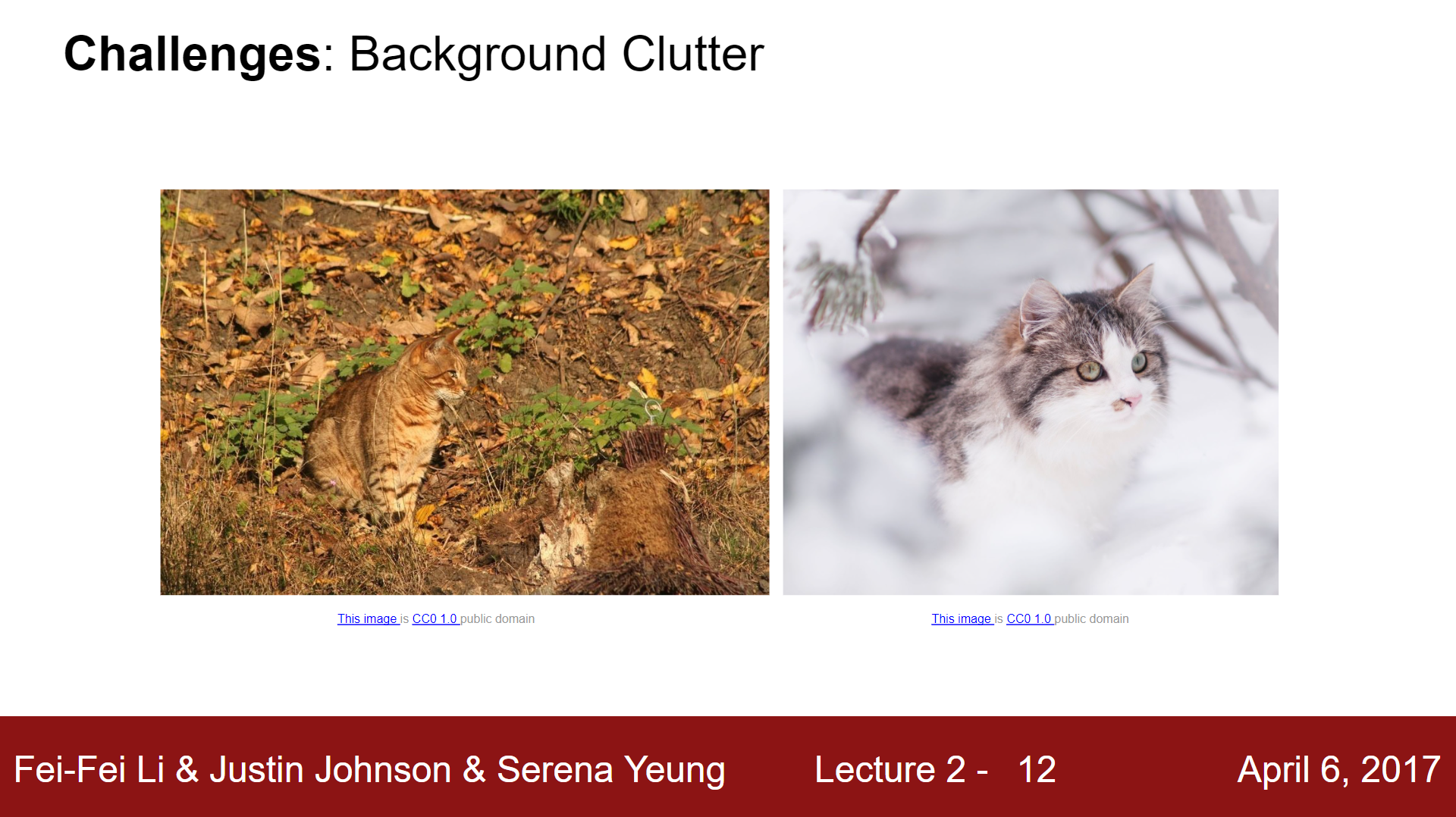
Background Clutter#
If the object blends into the background or vice versa, the object may be hard for a computer to distinguish.
Intraclass Variation#
Lastly, objects such as cats can have various species of different colors, sizes, and shapes.

Convolutional Neural Network#
To counter these challenges, we use something called a Convolutional Neural Network

Stanford’s cs231n 2018 Course: “Lecture 2 | Image Classification”
Created By: WHS Comp Sci Club Officers